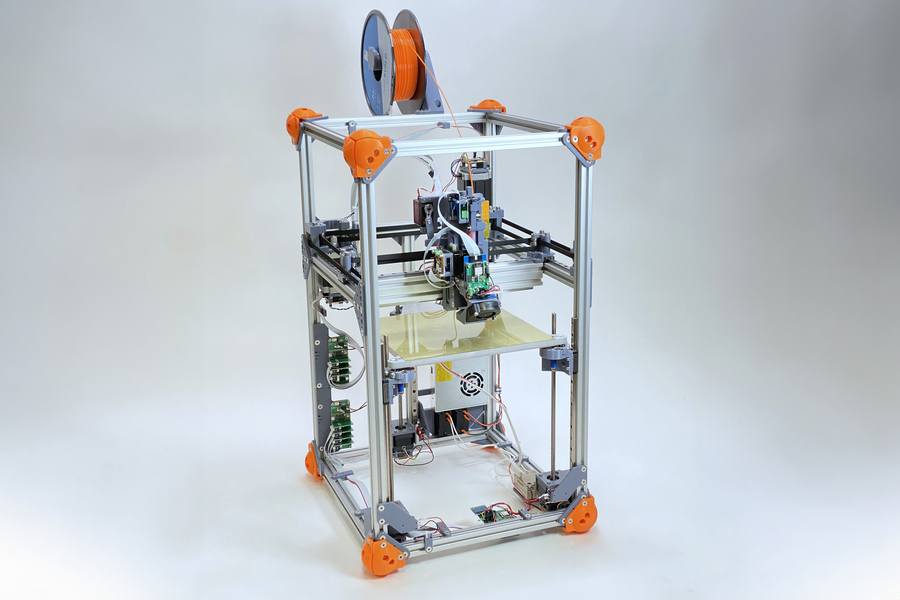

MIT’s new 3D printer can create its own parameters so that users don’t have to
A workforce of scientists have developed a brand new FDM 3D printer that may mechanically create parameters for unknown supplies.
Materials presets for mass-manufactured polymers could be discovered on most 3D printers. Nevertheless, the 3D printing parameters for sustainable and recycled supplies have to be manually adjusted. This trial and error course of could be irritating and time-consuming, limiting the adoption of environmentally pleasant filaments.
Consultants from MIT’s Middle for Bits and Atoms (CBA), the U.S. Nationwide Institute of Requirements and Expertise (NIST), and Greece’s Nationwide Middle for Scientific Analysis (Demokritos) are working to vary this.
The workforce constructed an extruder that may measure key filament data in the course of the 3D printing course of. This information was inputted right into a mathematical mannequin, which mechanically generated the fabric’s optimum 3D printing parameters.
In accordance with the workforce’s analysis paper, this new methodology may improve the adoption of distinctive FDM filaments which can be extra sustainable than hard-to-recycle fossil fuel-based polymers.
“On this paper, we display a technique that may take all these fascinating supplies which can be bio-based and created from varied sustainable sources and present that the printer can work out by itself the right way to print these supplies,” defined senior creator Neil Gershenfeld in an interview with MIT Information. “The aim is to make 3D printing extra sustainable.”


Mechanically producing materials parameters
3D printing with renewable and recycled supplies generally is a difficult course of. Attributable to variations of their properties, no two supplies are alike. As an illustration, bio-based polymers can function completely different plant mixtures based mostly on the season. This poses issues in relation to figuring out what 3D printing parameters to make use of.
The researcher’s new strategy overcomes these challenges by mechanically figuring out the optimum parameters for beforehand unknown supplies.
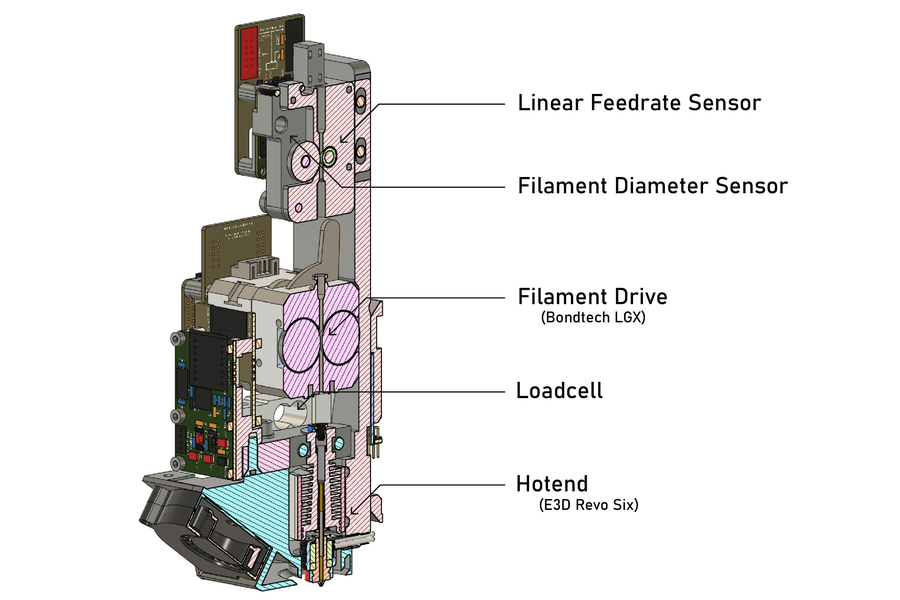
To attain this, the workforce adopted a 3D printer from the MIT lab and added three sensors to its extruder. A load cell was used to measure the strain utilized to the filament. Feed fee sensors tracked filament thickness and the speed at which materials was pushed into the 3D printer’s hotend.
A 20-minute check, designed to report a number of temperature and strain readings at completely different circulation charges, was carried out for every materials.
Throughout this check, the workforce set the 3D printer’s nozzle to 290℃, its highest potential temperature. The fabric was extruded at a set fee. Then, the heater was turned off whereas the filament continued to be pushed into the hotend.
The info was fed right into a mathematical perform that mechanically produced the perfect parameters. As soon as these are imputed into slicing software program, the fabric could be 3D printed with optimum outcomes.
The workforce experimented with six completely different supplies, a lot of which had been bio-based. Their technique mechanically generated parameters that enabled advanced objects to be efficiently fabricated.
Alysia Garmulewicz, an affiliate professor within the School of Administration and Economics on the College of Santiago, advised MIT Information that this new methodology “opens the door to the usage of recycled and bio-based filaments which have variable and unknown behaviors.”
Trying forward, the MIT-led workforce plans to instantly join its course of to 3D printing software program, eradicating the necessity to enter the parameters manually.

Researchers goal sustainable 3D printing
The worldwide 3D printing business is witnessing an rising give attention to sustainability, together with via the usage of extra environmentally pleasant supplies. That is particularly necessary in relation to FDM 3D printers. UK-based filament producer Filamentive just lately reported that this 3D printing course of produces 400,000 kg of plastic waste every year within the UK alone.
Scientists try to fight this with analysis into recycled 3D printing filaments. A workforce from the United Arab Emirates College developed a PLA filament created from recycled plastic and carbon fiber waste. The discarded materials was shredded, floor, blended, and melt-blended. These formulations had been then hot-pressed into dogbone specimens, with a common testing machine used to characterize the composite’s mechanical efficiency.
Having demonstrated that it’s potential to recycle PLA and carbon fiber concurrently, the researchers hope that others will examine extra environment friendly strategies of making recycled composites.
Bio-based filaments additionally provide the potential for greener FDM 3D printing. Beforehand, scientists on the Michigan Expertise College created 3D printable wooden filament from furnishings waste. Co-authored by open-source advocate Joshua Pearce, the analysis paper outlines a technique for combining this waste materials with PLA to create a wood-plastic composite (WPC).
With 150 tons of furnishings wooden waste produced every day in Michigan, the researchers acquired discarded MDF, LDF, melamine, and sawdust. This materials was lowered to powder and blended with PLA pellets to create the recycled filament. As soon as prepared, the workforce efficiently leveraged the fabric to 3D print a picket dice, a doorknob, and a drawer deal with.
What does the way forward for 3D printing maintain?
What near-term 3D printing tendencies have been highlighted by business consultants?
Subscribe to the 3D Printing Business publication to maintain updated with the most recent 3D printing information.
You can even observe us on Twitter, like our Fb web page, and subscribe to the 3D Printing Business Youtube channel to entry extra unique content material.
Featured picture exhibits the researchers’ 3D printer. This may generate parameters for unknown supplies. Picture through MIT Information.